What To Do With Waste in Cataract Surgery & Lowering the Carbon Footprint of Clinical Practices
A strong consensus exists among cataract surgeons and nurses that surgical waste is excessive and is driven by unnecessarily rigid regulation, product liability concerns, and manufacturers’ profit incentive.
The overwhelming majority of surgeons and nurses want more reusable options, more discretion on when to reuse products labelled for single use, and greater manufacturer consideration of carbon footprint.
It has been estimated that the healthcare sector accounts for approximately 10% of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, with the operating room being a leading source.
That the AECS has reduced the cost and carbon footprint of cataract surgery dramatically while achieving a lower POE rate than the United States average suggests that much of our surgical waste is excessive and unnecessary.
Because ophthalmology has the highest surgical volumes in medicine, we have an exceptionally important opportunity to educate and work with regulatory agencies and the surgical manufacturing industry to reduce needless OR waste.
The economic and environmental sustainability of cataract surgery worldwide may depend on our collaboration and leadership.
The Dutch Working Group on Sustainable Ophthalmology was founded in 2019. The aim of this group is to promote the transition to a sustainable clinical practice within our medical specialty. The group promotes research, provides information and coordinates action.
Based on current guidelines and scientific consensus, and respecting patient safety, the group has written directions for the safe and sustainable implementation of common ophthalmological procedures.
Examples are intravitreal injections, cataract surgery and patient gowns during surgery. The Dutch Ophthalmological Society has adopted and recommended these best practices, which are being adopted in a growing number of hospitals.
Recently, Dutch health insurance companies have shown interest in promoting these best practices. Intravitreal injections (IVIs) have revolutionised ophthalmology. With ever-increasing numbers of injections and a shift from reusable to disposable instruments, waste production has also soared.
Initially, we accepted the disposable custom-pack with plastic bowls, speculum, cotton buds and drape. However, seeing the overflowing waste bins after an afternoon of injections, we became frustrated.
We critically reviewed the literature on IVI procedures and concluded that we could do without drapes and forceps.
In consultation with the supplier, we omitted all plastic trays and bowls and replaced the polypropylene cover sheet with a crepe-paper wrap. This allowed for a much smaller plastic package.
In this way we reduced waste from 135.5 to 66.5 g per IVI and costs by 20%. In combination with the recycling of paper and clean plastics, the carbon footprint of a single IVI decreased from 0.68 kg CO2 to 0.17 kg CO2.
Performing 50 injections a day, the daily savings equate to 25.5 kg CO2, the equivalent of driving 116 km in a car. This reduced IVI set has been adopted by the Dutch Ophthalmological Society and is being implemented in more and more hospitals.
With over 400,000 annual injections nationwide, this small revision represents a large step forward in sustainable ophthalmology.
A call to action Last September, over 200 scientific medical journals simultaneously published a “Call for emergency action to limit global temperature increases, restore biodiversity and protect health.”
Participating journals ranged from the New England Journal of Medicine to the Croatian Medical Journal and from the Lancet to the Medical Journal of Australia.
The science is unequivocal: a global increase of 1.5°C above the pre-industrial average and the continued loss of biodiversity risk catastrophic harm to health.
Climate change is already impacting health in a myriad of ways, including death and illness from increasingly frequent extreme weather events such as heatwaves, storms and floods; the disruption of food systems; increases in zoonoses and food-, water- and vector-borne diseases; and mental health issues.
Furthermore, climate change is undermining many of the social determinants for good health, such as livelihoods, equality and access to healthcare and social support structures.
Despite the world’s necessary preoccupation with COVID-19, we cannot wait for the pandemic to resolve before taking action and should act now to rapidly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
What have ophthalmologists got to do with this? The healthcare sector is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. It is estimated that healthcare’s climate footprint is equivalent to 4.4% of global net emissions (2 gigatons of CO2 equivalent).
If the health sector were a country, it would be the fi fth largest emitter on the planet. So, the healthcare system itself contributes to a decline in public health. This message has been heard by leaders in the field.
During the recent COP26 UN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, a group of 50 countries, including the UK, the US, Germany and the Netherlands, committed to develop climate-resilient and low-carbon healthcare systems.
Previously, a target of net zero greenhouse gas emissions in the year 2030 was adopted by the UK National Health Service. In the Netherlands, all major players in the healthcare sector signed a Green Deal, committing to a 50% reduction in carbon footprint by the year 2030.
Important sources of healthcare carbon emissions are energy consumption, medication, disposables and patient travel. Although we are a small medical specialty, ophthalmology contributes signifi cantly to all these components.
We have the highest surgical volumes in medicine and use energy-consuming operating rooms (ORs); we increasingly use single-use products; we prescribe large amounts of (single-dose) eye drops; and we invite many patients to our clinics.
So, what can we do? Air conditioning in the operating room Are the highest ventilation standards really necessary for small-incision eye surgery? In the Netherlands, the recommendation for the OR air ventilation system for cataract surgery is an air change rate of at least six times per hour.
We should turn off the air conditioning when the OR is not in use. This may seem obvious, but it is not common practice in many hospitals.
Research shows that shutting down OR ventilation during off-duty periods does not appear to result in an unacceptably high particle count or microbial contamination of OR air, 30 minutes after the system is restarted.
Using an Eco-mode in OR air conditioning will save not only greenhouse gas emissions, but also money.
A critical factor is the source of electricity. The air conditioning accounts for more than 90% of the total energy use of the OR, so it is paramount to choose a renewable energy source instead of fossil-based energy. We should push our hospital management to buy 100% green energy.
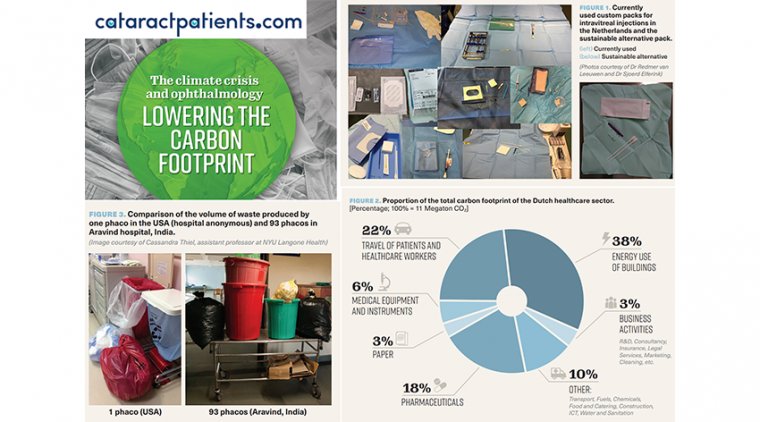
Waste in cataract surgery - One phaco procedure in the UK produces around 130 kg CO2, equivalent to a car ride of 500 km. More than 50% of this is due to procurement.
More recent data are not available, but the use of disposables has grown, adding to clinical waste production. Disposable instruments can account for 10–20 times as much waste as reusable items. All clinically contaminated waste must be incinerated or burned, which produces large amounts of greenhouse gases.
It is feasible to lower the carbon footprint of cataract surgery. This has been shown by the Aravind Eye Care System in southern India. Aravind performs around 1,000 surgeries per day. They generate 250 g waste and nearly 6 kg CO2 equivalents in greenhouse gases per phacoemulsification.
This carbon footprint is approximately 5% of that in the UK, with comparable visual acuity outcomes. Many differences can account for this low carbon footprint, including efficient, high-volume logistics and the reuse of instruments, protective equipment and medicines.
These differences do not affect infection prevention. In fact, the endophthalmitis risk after a phaco in Aravind is 0.01%, which is lower than the 0.04% in the US. This fact can partly be explained by the standard use of intracameral moxifloxacin in Aravind.
Ironically, this drug is not registered in the United States because of the lack of adequate randomised controlled trials. Rigid adherence to single-use material creates an excessive amount of surgical waste at a high cost, with no proven benefit in postoperative endophthalmitis risk.
Given the huge number of cataract operations worldwide, changes in the materials used will bring great environmental benefits. In the past two decades, operating theatres have transformed into disposable theatres; in every surgical specialty the majority of what is used is disposable.
The same holds for cataract surgery, where we have witnessed the transition to disposable I/A handpieces, disposable phaco-cartridges, disposable incision blades and preloaded IOLs. Some colleagues argue that disposables are safer than reusables and should therefore be promoted.
However, this claim has not been substantiated. The debate about disposable versus reusable surgical instruments should be settled by evidence. And the evidence shows that waste, greenhouse gas emissions and a shortage of commodities are a threat to future generations.
As long as there is no evidence that disposable instruments are safer for our patients, their use should be discouraged, not promoted.
Recently, a large survey among more than 1,300 US cataract surgeons and nurses showed that 93% believe that operating room waste is excessive and should be reduced.
More specifically, 78% believe that we should reuse more supplies and 87% want medical societies to advocate for reducing the surgical carbon footprint. Assuming comparable costs, 79% of surgeons preferred reusable over disposable instruments.
Medication It is important to consider the “reduce-reuse-recycle” rationale for medication use in ophthalmology as well. Tauber et al. showed that in cataract surgery a lot of medication used pre- and intraoperatively is discarded.
Discarded topical eye drops were the most costly, averaging 148 US dollars per case. Reasons for discarding these medications could be a lack of counselling for patients and lack of medication labelling, facility policies, and noncompliance with burdensome state requirements.
The largest component of pharmaceutical waste in the study of Tauber was antibiotic drops. As noted by the authors, given the lower rate of endophthalmitis after cataract surgery with the use of intracameral antibiotics, the use of antibiotic drops with cataract surgery is likely to decrease.
One should consider whether postoperative antibiotic eyedrops are still necessary when perioperative intracameral antibiotics are used. In many clinics it is policy to throw medication away after is has been opened for a single patient.
But it is important to examine the justification of these policies. Chambers showed that this justification is not scientifically based but rather a misinterpretation of the evidence. He explained that manufacturers of multiple-dose ophthalmic products are required (by the Federal Register) to use an antimicrobial preservative.
This antimicrobial preservative minimises the chances of injury to the patient should a contamination event occur. This additional protection also enables the drug product to be administered to multiple diff erent patients until the bottle’s stated expiration date.
Every ophthalmologist should consider whether it is possible to reuse multi-dose medication. Transport The COVID-19 pandemic has shown that remote care of patients via telemedicine is possible.
Telephone calls and video visits can be used to review test results, check on medication adherence or triage patients, and can replace check-ups for oculoplastic, neuro or paediatrics. Remote care can save greenhouse gas emissions.
Another lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic is that online meetings and conferences are feasible. Online meetings have pros and cons, but they certainly cause less greenhouse gas emissions than long-distance travel.
So, why not stick to virtual international meetings? Social interactions are undeniably important, but a national gathering to watch lectures and discussions abroad may be a reasonable alternative for many attendants.
Thousands of ophthalmologists flying abroad to attend a medical congress is not sustainable and not justifi able in these times.
Healthcare professionals are continuously trying to improve the quality of care as well as keeping the healthcare system aff ordable and accessible for future generations. If we do not lower the carbon footprint of our clinical practices, we will compromise the healthcare systems of our children and grandchildren.